Section 10 – Identification Device Certification
Overview
Introduction
This Section provides a general introduction to the principles and procedures developed for testing and certification of animal identification devices by ICAR.
On June 22, 2007 ISO appointed ICAR as the Registration Authority (RA) competent to register manufacturer codes used in the radio frequency identification (RFID) of animals in accordance with ISO 11784 and ISO 11785.
ICAR has administrative procedures in place for testing the conformance of RFID devices with respect to ISO 11784 and ISO 11785. Only those results coming from accredited test centres are recognized. In addition, ICAR offers evaluations on various quality and performance features of those devices that are tested for conformance with 11784/11785, and these evaluations are also available for conventional plastic ear tags.
Scope
Figure 1 provides a summary of the main elements of this guideline.
In summary, section 10 of the ICAR Guidelines covers the testing and certification procedures, from the submission of the application by a manufacturer to the publication of the certification on the ICAR website, and the re-certification and/or sampling of the product.
Figure 1. Scope of Section 10: Testing and certification of animal identification devices
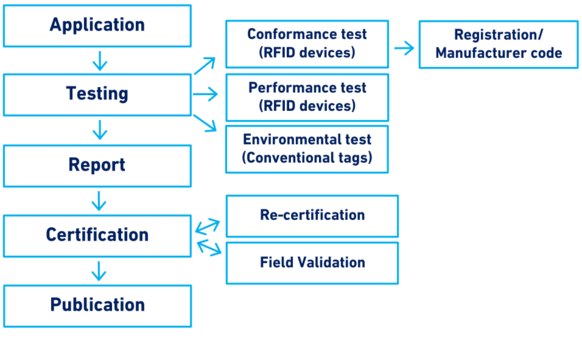
Application
The procedure for any type of test and certification starts with an application submitted by the manufacturer to the ICAR Secretariat. The Secretariat reviews the application, selects the test centre[1], issues an umbrella contract (only the first time that a test is requested) and issues the invoice that needs to be paid before the test starts. Financial transactions between manufacturers, test centres and ICAR are coordinated by the ICAR Secretariat. In order for the test to begin, the manufacturer sends all the necessary devices and accessories to the test centre. The devices and accessories remain the property of ICAR.
Testing
Testing of identification devices can be subdivided into four main categories as reported in Table 2.
RFID Conformance test (ISO 24631-1)
Conformance testing is required to demonstrate electronic transponders meet the specifications and standards in ISO 11784 and ISO 11785. The submission of identification devices to conformance testing is obligatory before they can be used in the official identification of animals.
Conformance tests are coordinated by the ICAR Secretariat. Acting as the RA on behalf of ISO, ICAR issues a Certificate of Conformance for RFID devices conforming with ISO 11784 and ISO 11785.
Details of the RFID Conformance test are described in Procedure 1, Section 10 ‘Conformance of RFID Transponders with ISO 11784 and ISO 11785’ available here.
RFID Performance test (ISO 24631-3)
Performance testing is an evaluation of the following characteristics of an RFID device: modulation amplitude, bit length stability, minimum activation field strength resonance frequency and amplitude voltage response (Vss). These RFID performance test results are not subject to pass or fail criteria but provide useful additional information on device behaviour when communicating with a reader. Acting as the RA on behalf of ISO, ICAR evaluates RFID devices through the RFID performance test and provides the report of the performance test to the manufacturer.
Device Composition and Environmental Performance test (ICAR)
ICAR offers a device composition and environmental performance test for both conventional and RFID external devices. The objective of these tests is to give extensive information on device durability and performance in diverse animal management conditions. Procedures will vary depending on the device type. ICAR shares the test report and ICAR certificate for devices in accordance with the specifications of the respective ICAR.
Details of the device composition and environmental performance test are described in Procedure 4, Section 10 ‘Testing of Conventional Plastic Ear Tags’ available here and Procedure 5, Section 10 ‘Testing of External RFID Devices’ available here.
Voluntary sampling of Animal Identification Devices
Voluntary sampling of Animal Identification Devices is a service for National Competent Authorities or other service users, other than manufacturers or their agents. The service is a quality verification service to ensure that devices available in the relevant market(s) remain compliant with the appropriate ISO and ICAR test protocols. Voluntary sampling does not lead to certification of the devices.
Details of the service are described in Procedure 6, Section 10 ‘Voluntary Sampling of Identification Devices’ available here.
Summary of Tests
Table 1 summarizes the categories of tests.
| Table 1. Categories for the testing of identification devices. | ||
| Test category | Test description | Link to test procedure |
| Conformance and Performance ISO 24631-1 | Conformance/performance test of transponder (incl. granting of manufacturer code) or transceiver |
Procedure 1, Section 10 ‘Conformance of Transponders with ISO standards’ Procedure 2, Section 10 ‘Granting of Manufacturer Code’ Procedure 3, Section 10 ‘Conformance of Transceivers with ISO standards’ |
| Composition and environmental performance – Conventional ear tags | Extended laboratory test |
Procedure 4, Section 10 ‘Testing of Conventional Plastic Ear Tags’ |
| Composition and environmental performance – External RFID devices | Extended laboratory test |
Procedure 5, Section 10 ‘Testing of External RFID Devices’ |
| Voluntary sampling | Partial test for certified devices available on the market. |
Procedure 6, Section 10 ‘Voluntary sampling of Identification Devices’ |
Test Centres
Testing is conducted by ICAR accredited test centres. Tests are contracted by the ICAR Secretariat to a specific test centre. The test centre is obliged to act according to the procedures laid down within the test protocols. In addition, all details associated with the testing phase, including the test results, must be kept strictly confidential. Test centres are regularly monitored by the ICAR Animal Identification Sub-Committee and their contact details are available here.
Manufacturer code
Following the first successful full conformance test, ICAR in its role as RA for ISO for the standards 11784/11785 – allocates to the manufacturer a code to be used only for products registered by ICAR. There are two types of manufacturer codes:
- Shared manufacturer code (900): can be granted to more than one manufacturer. A restricted range of identification codes is allocated to the registered product for exclusive use together with the shared manufacturer code.
- Unshared manufacturer code (901-998): can only be granted to one manufacturer following official proof that during two consecutive years the company has sold a minimum of one million (ICAR certified) transponders per year.
Note: the manufacturer code concerns only the certification of RFID devices. As regards conventional ear tags, ICAR allocates unique certification codes to the products that pass the Device composition and environmental performance test.
Report
Test centres prepare a confidential report of the test results and submit the report to the ICAR Secretariat. The Secretariat checks the report and forwards it to the manufacturer, together with the ICAR certificate in case of successful test. The report is also shared for information with the Animal Identification Sub-Committee.
Certification
The tests that lead to an ICAR certificate are:
- RFID Conformance test (ISO 24631-1).
- Device Composition and Environmental Performance test (ICAR).
Certificates are issued by the ICAR Secretariat and signed by the ICAR Chief Executive. They are sent to the manufacturer by e-mail. In the case of certificates of conformance, the Chair of the ISO/TC23/SC19/WG3 is copied so that ISO is informed about registered devices under the RA Agreement.
For other tests not subject to pass or fail criteria (e.g. Performance test), an official ICAR letter acknowledging the completion of the test is sent to the manufacturer.
Publication
All ICAR-certified devices are published on the ICAR website:
Devices whose certification has expired are removed from the webpage. A specific web page contains all the devices registered by ICAR in conformance with ISO standards 11784 and 11785. Devices listed in this webpage are never removed since the registration is valid for the lifetime of the device.
Table 2 summarizes the steps and responsibilities in the ICAR certification procedure.
| Table 2. Steps, actions and responsibilities in the ICAR certification procedure. | ||
| Step | Action | Responsibility |
| 1 | Application for testing of a device | Manufacturer or dealer of identification device |
| 2 | Acceptance of application, and issuance of umbrella contract and invoice | ICAR Secretariat |
| 3 | Testing and report compilation | ICAR test centres |
| 4 | Sharing of test results with the applicant | ICAR Secretariat |
| 5 | ICAR certification | ICAR Secretariat |
| 6 | Publication on the website | ICAR Secretariat |
Re-certification
After 5 years from the issuance of an ICAR certificate, the test can be repeated in order for the certification to be renewed for another 5 years. The device maintains its original product/certification code. The test protocols applied for the re-certification are:
- The limited test protocol for the RFID devices
- The preliminary assessment protocol for the conventional devices
Note: if the application for re-certification is submitted more than 5 years after the original certification, full test procedures are carried out.
The application process is the same as for any other tests. Once re-certified, the device remains on the ICAR website for another 5 years and the latest date of certification is indicated.
Voluntary sampling
At any given moment, Competent Authorities or other service users can apply for a sampling of certified devices found on the market. Devices are tested against the current ICAR standards and the results are compared with original or earlier results for the same devices. The test protocols used by the laboratories are:
- The limited test protocol for the RFID devices.
- The preliminary assessment protocol for the conventional devices.
The applicant may also request or specify additional test protocols, provided these are defined in other existing ISO or ICAR higher level test protocols.
It is required that the devices to be tested are collected from the local market stock by the applicant and not by the manufacturer.
Conditions for the use of ICAR certificates
- The conditions for the use of ICAR certificates are described in the respective procedures.
- If a device is certified by ICAR, the manufacturer may publish the certification of its device.
- ICAR certification does not guarantee that the device is suitable for all environments.
Note: A manufacturer must not use the ICAR logo for any purpose.
Appendices
Appendix A1. Application for RFID transponder Conformance test (ISO 24631-1) (link)
Appendix A2. Application for a manufacturer code allocation (link)
Appendix A3. Code of conduct (link)
Appendix A4. Application for RFID transponder Performance test (ISO 24631-3) (link)
Appendix A5. Application for RFID transceiver Conformance test (ISO 24631-2) (link)
Appendix A6. Application for RFID transceiver Performance test (ISO 24631-4) (link)
Appendix B1. Application for Device Composition and Environmental Performance test for conventional ear tags (link)
Appendix B2. Application for Device Change Notification (DCN) for conventional ear tags modified during the 5-year certification (link)
Appendix B3. Numbers for Reference Printing (link).
Appendix B4. Preliminary Test for Conventional Plastic Ear Tags (link).
Appendix B5. Laboratory Test for Conventional Plastic Ear Tags (link).
Appendix C1. Application for Device Composition and Environmental Performance test for external RFID devices (link)
Appendix C2. Application for Device Change Notification (DCN) for external RFID devices modified during the 5-year certification (link)
Appendix C3. Preliminary Test for External RFID Devices (link).
Appendix C4. Laboratory Test for External RFID Devices (link).
Appendix D1. Application for voluntary sampling of animal identification device (link) [1] Manufacturers also have the possibility to choose their preferred test centre.
Procedure 1: Conformance of Transponders
Foreword
ISO 24631 defines the test protocols for evaluating and verifying both the conformance (ISO 24631-1) and performance (ISO 24631-3) of RFID devices, and ISO 11784 defines the code structure. Only those results emanating from accredited and RA-approved test centres are recognized.
Introduction
ISO 11784 and ISO 11785 cover four RFID device types used for animal identification:
- Injectables: a small transponder able to be injected into an animal's body. The transponder is encapsulated in a biocompatible and non porous material, e.g. glass.
- Ear tag: a plastic covered transponder able to be fixed to an animal's ear using a locking mechanism which prevents the device from being removed without damaging it and rendering it unusable.
- Ruminal bolus: a transponder placed into a high specific gravity container orally administered to a ruminant animal where the device remains in the rumen of the animal due its high specific gravity which prevents its passing through the animal's digestive system.
- Tag attachment: a transponder covered by a primary protection layer but without its own locking system and is used only as an attachment to a visual ear tag or to another means of external animal identification, e.g. leg tag, collar, etc.
The tests managed by ICAR as RA are recognised by the Federation of European Companion Animals Veterinary Association (FECAVA) and WSAVA (World Small Animal Veterinarian Association) and as such can be applied to companion animals also.
The fee for all tests will be borne by the applicant.
References
ISO 11784 Agricultural equipment - Radio frequency identification of animals - Code structure
ISO 11785 Agricultural equipment - Radio frequency identification of animals - Technical concept
ISO 3166 Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions
The latest version of ISO Standards will always apply and these Standards can be downloaded from the ISO website (https://www.iso.org/store.html).
Procedures for verifying the ISO conformance of transponders
Application
A manufacturer can apply for:
- A full test; or
- A limited test; or
- A listing update.
A. A full test is mandatory in the following cases:
- When a non-RA registered manufacturer applies for a test.
- When a RA registered manufacturer uses a new silicon chip (Integrated Circuit) or implements new technology (HDX or FDX-B) in the transponder;
- When a RA registered manufacturer changes the coil technology (ferrite coils vs. air coils).
B. A limited test is applicable in the following cases:
- When a RA registered manufacturer inserts an ICAR certified transponder into a different primary transponder package.
- When a RA registered manufacturer uses the silicon chip of an ICAR certified transponder with different coil dimensions.
- When a RA registered manufacturer inserts an ICAR certified transponder with its original primary packaging into a different secondary packaging, e.g. a glass transponder into a bolus or a glass transponder into an ear tag.
C. A listing update is applicable in the following case:
- When a RA registered manufacturer intends to use an ICAR certified transponder without any modification. In this case the applicant must deliver a copy of the original test report along with a written confirmation from the ICAR registered manufacturer who originally submitted the transponder under question for certification by ICAR.
To apply for an ISO transponder conformance test, the manufacturer has to complete the test application form given in Appendix A1 (Application for RFID transponder Conformance test (ISO 24631-1)) which is available here.
The completed application must be emailed in PDF format to the ICAR secretariat at manufacturers@icar.org.
The manufacturer may choose their preferred ICAR accredited test centre. The manufacturer is required to submit to the test centre:
- 50 transponders for a full test, or
- 10 transponders for a limited test, or
- 10 transponders for a listing update.
The submitted transponders must have the ICAR test code of 999 or the existing manufacturer's code for a full test. The manufacturer can freely choose the transponder codes, but duplicate codes are not allowed. The manufacturer must provide a list of the transponder codes in decimal format.
Every specimen in a batch submitted for RFID testing (ISO24631-1 and/or ISO24631-3) must contain identical internal electronic components (coil and other components). Mixing of technologies (integrated circuit, capacitors, coils) within a single batch is prohibited. Likewise, when an electronic identifier is approved by ICAR, based on the results of testing, all identifiers that are released for sale must contain the same components as the test specimens. If changes are made to an identifier model after approval, the test requirements of ISO24631-1 section 6.1 must be met.
The test centre will test the transponders for compliance with ISO 11784 and ISO 11785. All tested transponders must be readable by the laboratory reference transceiver. The codes read by the laboratory reference transceiver must comply with ISO 11784 and the identification codes must be on the list of codes provided by the manufacturer.
The test centre will prepare a confidential report of the test results and will send the report to the ICAR secretariat. For a limited test or a listing update, the test report will contain only a summary of the test results.
The ICAR Secretariat will send the test report to the manufacturer and, in the case of a successful Conformance test result, an official ICAR letter of certification signed by the ICAR Chief Executive will also be sent to the manufacturer, with a copy to the ISO/TC23/SC19/WG3 Chair.
ICAR as RA issues a product code for each type of transponder successfully tested, including the listing update.
All electronic transponders submitted in an application will be kept by the test centre as reference transponders.
ICAR as RA maintains a public register on the ICAR website which lists all products registered and ICAR certified. A photograph of the certified device is included in the listing.
Conditions for the right to use an ICAR certificate for transponders (conformance test)
Upon successful completion of the Conformance test, ICAR will grant a device certificate valid for five years.
The ICAR certification of a transponder confirms the transponder's compliance with the code structure and the technical concepts given in ISO 11784 and ISO 11785.
The manufacturer must maintain a database register of all ICAR certified transponders sold. The manufacturer must require the initial purchasers of their ICAR certified transponders to also maintain a database register of their purchased product and require all subsequent purchasers to do the same until the transponder is applied to an animal.
The ICAR certificate is valid only for the transponder successfully tested and certified by ICAR. A manufacturer must not utilise the ICAR certificate for a transponder:
- Which is not manufactured by them; and / or
- Which does not comply in all respects with the ICAR certificate, including (but not limited to):
- Maintaining identical packaging (both primary and secondary) of the certified transponder.
- Maintaining identical technology and manufacturer of the certified transponder.
- Maintaining the identical transponder to the certified transponder.
- Which utilises the manufacturer code of another manufacturer;
- Which is supplied to or intended to be supplied to a person ("the receiver") who will market the transponder as if manufactured by them, unless:
- The receiver has obtained ICAR registration under this process; and
- The transponder bears either the shared manufacturer code or the unshared manufacturer code of the receiver.
Once the ICAR certification has been granted, the manufacturer will be responsible to:
- Keep an accurate and detailed log of all changes to their product and this log must be available to ICAR upon request. This log must include details of in-house performance measurements and Quality Assurance testing showing the amended product has maintained or enhanced its quality and performance.
- Submit the product for re-certification before the expiration of its current ICAR certification. The manufacturer must apply for re-certification not earlier than 6 months before the expiration of the certificate and no later than 5 months after the expiration of the certificate.
- Understand that ICAR may take sample products from the marketplace and test its conformance against the conformance of the device the manufacturer originally submitted, should ICAR suspect a breach of the signed ICAR Code of Conduct or a product change that has not been subjected to the tests outlined in this document - Procedure 1, Section 10 ‘Conformance of Transponders with ISO standards’.
Should the manufacturer fail to meet any or all of the above conditions for the use of the ICAR certificate, actions may be taken by ICAR in its role as Registration Authority for ISO according to the ISO standard 24631-1.
In cases of disputes regarding the conditions listed above or the use of an ICAR certificate, the decision of ICAR as RA will be binding.
ICAR as RA will distribute an advice notice regarding any manufacturer that distributes transponders in conflict with the certification procedure.
Procedure 2: Granting of Manufacturer Code
Introduction
According to ISO 11784 "... it is a national responsibility to ensure the uniqueness of the national identification code". Where countries have not undertaken efforts to set up a procedure for the allocation and registration of the national identification code, a manufacturer code must be used instead of a country code to ensure a worldwide uniqueness of identification codes. ISO has appointed ICAR as the RA to allocate manufacturer codes in conformance with ISO 11784.
A manufacturer code can be granted to more than one manufacturer and this code is known as a shared manufacturer code. A shared manufacturer code can be granted by ICAR as RA if the manufacturer's RFID device has successfully completed a full conformance test. When a shared manufacturer code is granted, ICAR as RA also allocates a restricted set of identification codes for exclusive use with the shared manufacturer code. The identification codes allocated in combination with the shared manufacturer code are unique. ICAR as RA must ensure this uniqueness by applying appropriate procedures for the assignment and registration of allocated identification codes. If necessary, additional sets of identification codes can be assigned to the manufacturer by request. The size of the sets of allocated identification codes is determined on consensual agreement with the manufacturer and ICAR.
An unshared manufacturer code will only be granted to a manufacturer providing proof to the Registration Authority that during two consecutive years the company has sold a minimum of one million (ICAR certified) transponders per year. This proof must be sourced from their sales records and certified by their external auditor of accounts or a notary public.
Manufacturer Code Application Procedure
A manufacturer who applies for a conformance test for the first time has to also apply for a manufacturer code and sign a Code of conduct.
The first full test application must consist of a completed test application form (Appendix A1), a completed application form for a manufacturer code (Appendix A2), and the signed "Code of conduct" (Appendix A3). By signing the application form and the Code of conduct, the manufacturer agrees to fulfil the conditions described in this document and to accept the charges for this procedure.
The completed application must be emailed in PDF format to the ICAR secretariat at manufacturers@icar.org.
ICAR maintains a public register listing all registered manufacturers and the shared/unshared manufacturer codes granted.
Conditions for the right to use the manufacturer code
The manufacturer can only use their manufacturer code for products registered by ICAR as RA.
In disputes regarding the conditions of manufacturer code use, the decision of ISO/TC 23/SC19 will be binding.
For further reference, ISO 11784:1996/Amd 2:2010 (Radio frequency identification of animals — Code structure — Amendment 2: Indication of an advanced transponder) can be downloaded from the ISO web site (https://www.iso.org/store.html).
The use of Manufacturer codes and Country codes
Manufacturer codes (900-998 series) should only be used in connection with electronic identification (RFID) devices, in accordance with ISO 11784 and Section 10 of these Guidelines, including Appendix A3 Code of Conduct.
Where a national competent authority has assumed the responsibility for ensuring and maintaining the uniqueness of the RFID identification code for a specific species in that country, the ISO 3166 3-digit numeric country code may be used in place of the manufacturer code in the electronic identity or RFID of that specific species of animal.
The use of manufacturer codes in the International Identity used for genetic evaluation purposes is discouraged (Section 9 – Dairy Genetic Evaluations).
Procedure 3: Conformance of Transceivers with ISO Standards
Scope
This section refers to ISO 24631-2 and ISO 24631-4, regarding the test procedures to verify the compliance of RFID transceivers to the operating characteristics outlined in ISO 11784 and ISO 11785.
References
The titles of standards referred to in this document are as follows:
ISO 11784 Agricultural equipment – Radio frequency identification of animals - Code structure
ISO 11785 Agricultural equipment – Radio frequency identification of animals - Technical concept
ISO 3166 Codes for the representation of names of countries
The latest version of ISO Standards will always apply and these Standards can be downloaded from the ISO website store (https://www.iso.org/store.html).
Procedure 4: Testing of Conventional Plastic Ear Tags
Introduction
This section will guide the manufacturer through the steps of obtaining and retaining ICAR certification for a conventional permanent plastic ear tag.
The ICAR procedures for testing the performance and reliability of permanent identification devices consider, but are not limited, to the following issues:
- Ease of application and use.
- Efficiency of animal recognition.
- Durability and tamperproof quality.
- Animal welfare and human health.
The following procedures focus on testing the ear tag design, the print quality and, if requested, the ear tag machine readability.
The testing procedure is composed of three distinct phases:
- Phase 1: Manufacturer's application (section 5.1).
- Phase 2: Preliminary Assessment (section 5.2).
- Phase 3: Laboratory Test (section 5.4).
These test procedures must be carried out by an ICAR accredited test laboratory (list available here). The costs for these test procedures will be borne by the device manufacturer.
When an ear tag is certified by ICAR, the manufacturer will be authorized to state that tags of that particular design and printing method are ICAR certified. ICAR certification does not imply that the tag is suitable for all environments or that its machine-readable characteristics are satisfactory for all uses. It is the manufacturer's responsibility to comply with the requirements of the relevant jurisdictions.
A successfully tested and certified product can have its certification withdrawn if the product fails to comply with the requirements described in this section. ICAR and/or national authorities may randomly take samples of certified tags from the market and subject them to testing to ensure certified ear tags continue to meet ICAR certification criteria. The manufacturer will be required to meet the costs of these assessments should the product fail to meet ICAR standards.
The manufacturer must advise ICAR of any changes made affecting the performance of ICAR certified products which could alter their previous test results. The manufacturer must also inform ICAR of any change to the composition or the print quality of a certified ear tag.
Users of ear tags and / or potential users of ear tags are encouraged to access the list of certified tags found on the ICAR web site (the page available here).
Scope
This section describes the evaluation procedures for measuring the composition and the performance of conventional permanent plastic ear tags which may include machine readable printing.
When a manufacturer submits an ear tag to ICAR for testing, they may also choose to have the machine readability of the ear tag evaluated according to this protocol. If such request is not explicitely made, then only the visual readability will be evaluated.
Successful completion of the procedures described in this section will result in the ICAR certification of the ear tag as a device recommended by ICAR for animal identification purposes. ICAR certified ear tags are published on the ICAR website here as certified visual identification devices. Only the tags on this page are ICAR certified.
Figure 2 gives a summary of the main elements of the testing and certification process of conventional ear tags.

References
| Table 3. References to relevant standards. | |
| ISO 175 | Resistance of thermoplastics to liquids |
| EN 1122 | Plastics - Determination of cadmium - Wet decomposition method |
| ISO 1817 | Resistance of vulcanized elastomers to liquids |
| ISO 4650 | Rubber - Identification - Infrared spectrometric method |
| ISO 9924 | Determination of composition of vulcanized elastomers |
| ISO 11357 | Plastics - Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) |
| ISO 9352 | Plastics - Determination of resistance to wear by abrasive wheels |
| ISO 527-1 | Plastics - Determination of tensile properties part 1: General principles |
| ISO 37 | Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic - Determination of tensile stress-strain properties |
| ISO 4611 | Plastics - Determination of the effects of exposure to damp heat, water spray and salt mist |
| EN ISO 4892-2 | Plastics - Methods of exposure to laboratory light sources - Part 2: Xenon-arc lamps |
| ISO 15416 | Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture techniques - Bar code print quality test specification; Linear symbols |
| ISO 11664-4 | Colorimetry - Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour space |
The latest version of the above references will always apply.
Definitions
Certification code
A certification code is an alpha-numeric code consisting of "A", followed by three numbers. The certification code is used to identify and register an ear tag model that has successfully passed the testing procedure. This code may be embossed on all ICAR certified ear tags for official identification. The placement of the certification code on the ear tag should conform to the relevant jurisdictional requirements in whatever locality the ear tag is sold.
Certified ear tag
A certified ear tag is an ear tag described in the Application Form that was submitted to the ICAR accredited test centre where it successfully passed the testing procedures and was thus certified by ICAR.
Ear tag
An ear tag is deemed to be composed of three principal features:
- The front plate which is often, but not always, the "female" component of an ear tag combination. The front plate is designated as such because it will be in the front of the animal's ear when the ear tag combination is applied correctly.
- The rear plate which is often, but not always, the "male" component of an ear tag combination. The rear plate is designated as such because it will be at the back of the animal's ear when the ear tag combination is applied correctly.
- The locking mechanism which comprises of the locking gap in the female component of an ear tag and the pin of the male component of the ear tag combination.
Manufacturer
The manufacturer is the company or person submitting the application for the testing of an ear tag and has accepted the ICAR conditions for certification of conventional permanent plastic ear tags as outlined in section 5.4.6.
Reference colour
The colour of the ear tags used in the laboratory tests must be yellow and the colour of the printing must be black. The manufacturer must print a uniform solid block 10mm x 10mm in the same colour as the colour of the printing on the tag.
Reference number
Printing must be composed of four different and predefined figures (from 0 to 9) as outlined in Appendix B3. The font style and size must replicate precisely the font style and size the manufacturer commonly uses on that tag within the market.
For the ear tags where machine readability will be assessed, a 12-digit barcode must be printed on the tags in addition to the reference number. The 12-digit barcode consists of the three numbers of the test code as defined in section 4.7 followed by zeroes and the reference number.
Test code
The test code is an alpha-numeric code consisting of "T", followed by 3 numbers.
The test code is used to identify and register an ear tag model being tested at the laboratoryunder the approval procedure. This code must be printed or engraved on all ear tags undergoing testing during the approval procedure.
Tested Ear tag
A tested ear tag is an ear tag described in the Application Form that was submitted to the ICAR accredited test centre and subsequently tested.
ICAR testing and certification procedure
Phase 1: Manufacturer's application
To submit an ear tag for ICAR testing within the scope of the tests described in this section, the manufacturer must complete an application and email it in PDF format to the ICAR secretariat at manufacturers@icar.org
The application must consist of the Application Form (Appendix B1 or Appendix B2):
- Appendix B1 is the application form for the certification of a new device or re-certification of an already certified device.
- Appendix B2 is the application form for the certification of a device modified during its certification. (Please refer to section 6 for information on the Device Change Notification)
Copies of the required application forms can be obtained from the ICAR website or from the ICAR Secretariat.
When a manufacturer chooses to have the machine readable printing on the ear tag evaluated, the manufacturer must indicate this choice on the completed Application Form. The application should also specify the symbols (language) used on the tag, e.g. Quick Response (QR) Model 2, Data Matrix (DM) ECC 200, Aztec, Code 128, Code 39 or Interleaved 2 of 5. The applicant should also indicate if the AIM (Automatic Identification Manufacturers International Inc) quality standards (code dimensions) have been met.
By signing the application form, the manufacturer agrees to fulfil the conditions of ICAR testing, certification and payment obligations and also acknowledges the ongoing monitoring and assessments for certified ear tags.
Phase 2: Preliminary assessment
To assess conformance of the ear tags with the information given in the application form and to also detect any major failure, e.g. damage of the tag at application, possible unlocking without deformation, inappropriate animal welfare design etc., the ear tags will be submitted to a Preliminary Assessment.
The Preliminary Assessment procedure is also applied to a device for which the manufacturer is requesting re-certification.
Refer to Appendix B4 for details.
Conclusion of the Preliminary assessment
The test centre will prepare a comprehensive report detailing the results of the Preliminary Assessment. This report will be submitted to the ICAR Secretariat, who will then forward the test report to the manufacturer.
If the Preliminary Assessment is successful, then the manufacturer will be asked to confirm their willingness to proceed to the Laboratory test.
If a device has not performed satisfactorily, ICAR will provide the manufacturer with the test report and indicate the reasons for the tag's failure.
Phase 3: Laboratory Test
Assigning a test centre
Following the successful completion of the Preliminary Assessment and the decision of the manufacturer to proceed to the Laboratory Test, the ICAR Secretariat will assign one of the accredited test centres to carry out the Laboratory Test. The manufacturer’s preferred approved test centre may be taken into consideration.
Granting of a test code
A specific test code will be allocated by ICAR for the ear tag undergoing testing. The manufacturer will be advised of the test code, which must printed or engraved on each ear tag provided for the Laboratory Test.
Manufacturer requirements
At the commencement of the Labortory Test, the manufacturer must deliver the following items to the assigned test centre:
- 200 yellow ear tags with the test code number and the reference printing applied (including the uniform solid block described in 4.5). For tags where the machine readability is to be assessed, a 12-digit barcode must also be printed on the ear tag. Note: the manufacturer will be allocated 25 reference numbers to print on the 200 ear tags, i.e. 8 tags per reference number (Appendix B3).
- One tag applicator or an equivalent device supplied for the application of devices to animals.
- A statement specifying the nature of the polymer used for the ear tag, e.g. thermoplastic elastomers, vulcanized elastomer etc.
Test procedure
The test procedure to be followed for Phase 3: Laboratory Test is described in Appendix B5.
Conclusion of the laboratory test
The test centre will prepare a test report and will submit it to the ICAR Secretariat. All information collected during the laboratory tests will remain confidential and only disclosed to the manufacturer of the ear tag.
Upon the successful completion of the Laboratory Test, ICAR will send the test report and an official letter to the manufacturer granting ICAR certification for that ear tag.
If the manufacturer had requested an evaluation on the machine readability of the ear tag, then this evaluation will also be included in the test report.
Each test report on a successfully tested ear tag will include a summary sheet with an evaluation of the appropriate suitability of the ear tag for various production systems and / or environmental conditions.
If the Laboratory Test results are unsatisfactory, ICAR will send the manufacturer the test report indicating the reasons for the failure.
All test reports are shared with ICAR’s Animal Identification Sub-Committee for information.
ICAR conditions for certification of conventional permanent plastic ear tags
- Upon successful completion of the ICAR test procedures described above, ICAR will grant a device certificate valid for five years and a certification code.
- This certification is valid only for the specific plastic ear tag type successfully tested and certified by ICAR.
- A manufacturer cannot utilise the ICAR certification for a plastic ear tag:
- Which is not manufactured by them; or
- Which does not comply in all respects to the ICAR certification, which includes maintaining an identical tag type to the certified tag.
- Once the ICAR certificate has been granted, the manufacturer will be responsible to:
- Keep an accurate and detailed log of all changes to their product and this log must be available to ICAR upon request. This log must include details of in-house performance measurements and Quality Assurance testing showing the product has maintained or enhanced its quality, performance and material composition.
- Submit the product for a Device Change Notification (DCN – Appendix B2) if changes are made to the device during its 5-year certification period. The modified device will have a new certification code, while the manufacturer will need to declare if the modified device will replace the existing one or if the two devices are going to co-exist. Every DCN application will be reviewed individually by ICAR and the designated laboratory, and ICAR shall decide if a partial test is applicable, or if the range of the modifications is such that a full test is required. Note: The request for DCN is not applicable to all types of changes to a device. Manufacturers are requested to contact the ICAR Secretariat (manufacturers@icar.org) for guidance before they apply for DCN.
- Submit the product for re-certification before the expiration of its current ICAR certification. The manufacturer must apply for re-certification no earlier than 6 months before the expiration of the certificate and no later than 5 months after the expiration of the certificate.
- Understand that within the 5 year timeframe, ICAR may take sample products from the market and test their performance against the performance of the certified device, should ICAR suspect a product change that has not been subjected to the tests outlined in this Procedure 4 of Section 10 of the ICAR Guidelines, or any other breach of the conditions described in this chapter.
- Should the manufacturer fail to meet any or all the above certification conditions, ICAR may withdraw the certification.
- In disputes regarding the conditions above or the use of a certificate, the decision of ICAR will be binding.
- ICAR will distribute an advice notice regarding any manufacturer distributing products in conflict with the testing and certification procedures outlined in this Procedure 4 of Section 10 of the ICAR Guidelines.
Procedure 5: Testing of External RFID Devices
Introduction
This section will guide the manufacturer through the steps of obtaining and retaining ICAR certification for an external permanent radio frequency identification (RFID) device.
The ICAR procedures for testing the performance and reliability of external permanent RFID devices consider, but are not limited to, the following issues:
- Ease of application and use.
- Efficiency of animal recognition.
- Durability and tamper-evidence.
- Animal welfare and human health.
Only external RFID devices designed as permanent electronic identification devices are covered in this procedure 5 of Section 10 of the ICAR Guidelines.
The testing procedure is composed of three distinct phases:
- Phase 1: Manufacturer’s Application (section 6.5.1 )
- Phase 2: Preliminary Assessment (section 6.5.2)
- Phase 3: Laboratory Test (section 6.5.3)
These test procedures must be carried out by an ICAR accredited test laboratory. The fees for these test procedures will be borne by the device manufacturer.
When an ear tag is certified by ICAR, the manufacturer will be authorized to state that tags of that particular design and printing method are ICAR certified. ICAR certification does not imply that the tag is suitable for all environments or that its machine-readable characteristics are satisfactory for all uses. It is the manufacturer's responsibility to comply with the requirements of the relevant jurisdictions.
A successfully tested and certified product can have its certificate withdrawn if the product fails to comply with the requirements described in this section. ICAR and/or national authorities may randomly take samples of certified devices from the market and subject them to testing to ensure certified devices continue to meet ICAR certification criteria. The manufacturer will be required to pay the costs of these assessments should the product fail to meet ICAR standards.
The manufacturer must advise ICAR of any sub-standard performance of ICAR certified products not in accordance with their previous test results. The manufacturer must also inform ICAR of any change to the composition of a certified RFID device.
Users (and/or potential users) of external RFID devices are encouraged to access the list of certified RFID devices found on the ICAR web site here.
Scope
This section describes the evaluation procedures for measuring the composition and the performance of external RFID devices.
Successful completion of the procedures described in this section will result in the ICAR certification of the tested RFID device as a device recommended by ICAR for animal identification purposes. ICAR certified RFID devices are published on the ICAR web site (here).
Figure 3 gives a flowchart, showing the main elements of the testing and certification process of external RFID devices

References
| Table 4. References to relevant standards. | |
| EN 1122 | Plastics - Determination of cadmium - Wet decomposition method |
| ISO 4650 | Rubber - Identification - Infrared spectrometric method |
| ISO 9924 | Determination of composition of vulcanized elastomers |
| ISO 11357 | Plastics - Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) |
| ISO 527-1 | Plastics - Determination of tensile properties part 1: General principles |
| ISO 37 | Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic - Determination of tensile stress-strain properties |
| ISO 11664-4 | Colorimetry - Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour space |
| ISO 7724 | Paints and Varnishes – Colorimetry |
| EN ISO 4892-2 | Plastics - Methods of exposure to laboratory light sources Part 2: Xenon-arc lamps |
| EN/IEC 60068-2-1 | Environmental testing - Part 2-1: Tests - Test A: Cold |
| EN/IEC 60068-2-2 | Environmental testing - Part 2-2: Tests - Test B: Dry heat |
| EN/IEC 60068-2-32 | Environmental testing - Part 2-32: Tests - Test Ed: Free fall |
| ISO 4611 | Plastics - Determination of the effects of exposure to damp heat, water spray and salt mist |
| ISO 11785 | Radio frequency identification of animals - Technical concept |
| ISO 24631-1 | Radio frequency identification of animals - Part 1: Evaluation of conformance of RFID transponders with ISO 11784 and ISO 11785 |
| ISO 24631-3 | Radio frequency identification of animals - Part 3: Evaluation of performance of RFID transponders conforming with ISO 11784 and ISO 11785 |
The latest version of the above references will always apply.
Definitions
Certification code
A certification code is an alpha-numeric character string consisting of the letter “A”, followed by three numbers. The certification code is used to identify and register an RFID device that has successfully completed the testing procedure. This code may be embossed or printed on all ICAR certified RFID devices for official identification. The placement of the certification code on the device should conform to the relevant jurisdictional requirements in whatever the locality the RFID device is sold.
Certified RFID device
A certified RFID device is an RFID device described in the Application Form that was submitted to the ICAR accredited test centre where it successfully passed the testing procedures and was thus certified by ICAR.
Manufacturer
The manufacturer is the company that produces the device and submits the application for the testing of an RFID device and has accepted the conditions of ICAR for the certification of external RFID devices as outlined in section 7.
Reference colour
The colour of the external RFID device used in the laboratory tests must be yellow and the colour of the printing must be black. On the test samples, preferably on the rear part, the manufacturer must print a uniform solid block of 10mm x 10mm in the same colour as the colour of the printing on the device. Should the surface area of the device be too small to accommodate the printing of a 10mm x 10mm solid block, then a uniform solid block of 5mm x 20mm is acceptable. This printing may be on the female tag plate or on the male tag plate (sometimes known as the pin).
Reference ID codes
The transponders of the RFID devices submitted to the laboratory test must be programmed with the test code of 999 followed by zeroes and a sequential numerical code as per the following:
- For the Phase 1 Preliminary Assessment, the sequential numerical code range will be: 001 - 130.
- For the Phase 2 Laboratory Test, the sequential numerical code range will be: 201 - 400.
- The reference ID code programmed into each transponder must be printed on the front part of each device. The font style and size must replicate precisely the font style and size the manufacturer commonly uses on that device within the market. This font size and style must be specified in the application form (Appendix C1 or Appendix C2).
RFID ear tag
An RFID ear tag is a radio frequency identification (RFID) external device able to be fixed to an animal’s ear and deemed to be composed of three principal features:
- The front part which is often, but not always, the “female” component of an ear tag combination. The front part is designated as such because it will be in the front of the animal’s ear when the ear tag combination is applied correctly. It will often, but not always, contain the transponder.
- The rear plate which is often, but not always, the “male” component of an ear tag combination. The rear plate is designated as such because it will be at the back of the animal’s ear when the ear tag combination is applied correctly.
- The locking mechanism which comprises of the locking gap in the female component of an ear tag and the pin of the male component of an ear tag combination.
RFID leg tag
An RFID leg tag is a radio frequency identification (RFID) external device able to be permanently fastened to an animal’s lower leg.
Tested RFID device
A tested RFID device is a device described in the Application Form that was submitted to the ICAR approved test centre and subsequently tested.
ICAR Testing and Certification Procedure
Phase 1 Manufacturer’s Application
To submit an external RFID device for ICAR testing within the scope of the tests described in this section, the manufacturer must complete an application and email it in PDF format to the ICAR secretariat at [[1]]
The application must consist of the Application Form (Appendix C1 or Appendix C2):
- Appendix C1 form is the application form for the certification of a new device.
- Appendix C2 is the application form for the certification of a device that has been modified during its certification period. (Please refer to section 7 for information on the Device Change Notification)
Copies of the required application form can be obtained from the ICAR web site (here) or from the ICAR Secretariat.
By signing the application form, the manufacturer agrees to fulfil the conditions of ICAR testing, certification and payment obligations and also acknowledges the ongoing monitoring and assessments applicable for certified RFID devices.
Phase 2: Preliminary Assessment
To assess conformance of the ear tags with the information given in the application form and to also detect any major failure, e.g. damage of the tag at application, possible unlocking without deformation, inappropriate animal welfare design etc., the ear tags will be submitted to a Preliminary Assessment.
The Preliminary Assessment procedure is also applied to a device for which the manufacturer is requesting re-certification
Test procedures
Refer to detailed test procedure in Appendix C3. Preliminary Test for External RFID Devices (link).
Conclusion of the Preliminary assessment
The test centre will prepare a comprehensive report detailing the results of the submitted external RFID devices’ performance. This report will be submitted to the ICAR Secretriat, who will then forward the test report to the manufacturer.
If the Preliminary assessment is successful, then the manufacturer will be asked to confirm their willingness to proceed to the Laboratory Test.
If a device has not performed satisfactorily, ICAR will provide the manufacturer with the test report and indicate the reasons for the device’s failure.
Phase 3 Laboratory Test
Assigning a Test Centre
Following the successful completion of the Preliminary Assessment and the decision of the manufacturer to proceed to the Laboratory Test, the ICAR Secretariat will assign one of the accredited test centres to carry out the Laboratory Tests. The manufacturer’s preferred approved test centre may be taken into consideration.
Granting of a Test Code
A specific test code will be allocated by ICAR for the RFID device undergoing testing. The manufacturer will be advised of the test code, which must be printed or engraved on each device provided for the Laboratory Test.
Manufacturer Requirements
At the commencement of the Laboratory Test, the manufacturer must deliver the following items to the assigned test centre:
- 200 external RFID devices programmed with the reference ID codes and the reference printing (Appendix B3).
- One tag applicator or an equivalent device supplied for the application of devices to animals.
- A statement specifying the nature of the polymer used for the RFID device, e.g.: thermoplastic elastomers, vulcanized elastomer etc.
Test procedure
Refer to detailed test procedure in Appendix C4. Laboratory Test for External RFID Devices (link).
Conclusion of the laboratory tests
The test centre will prepare a test report and will submit it to the ICAR Secretariat. All information collected during the laboratory tests will remain confidential and only disclosed to the applicant.
Upon the successful completion of the Laboratory Testing, ICAR will send the test report and an official letter to the manufacturer granting ICAR certification for that RFID device.
Each test report on a successfully tested RFID device will include a summary sheet with an evaluation of the appropriate suitability of the RFID device for various production systems and / or environmental conditions.
If the Laboratory Test results are unsatisfactory, ICAR will send the manufacturer a test report indicating the reasons for the failure.
All test reports are shared with ICAR’s Animal Identification Sub-Committee for information.
ICAR conditions for certification of permanent external RFID devices
- Upon successful completion of the ICAR test procedures described above, ICAR will grant a device certificate valid for five years and a certification code .
- The certification is valid only for the specific external RFID device type successfully tested and certified by ICAR.
- A manufacturer cannot utilise the ICAR certification for an RFID device:
- Which is not manufactured by them; or
- Which does not comply in all respects to the ICAR certification (but not limited to):
- Maintaining identical technology and the manufacturer of the certified tag;
- Maintaining an identical RFID device to the certified tag;
- Once the ICAR certification has been granted, the manufacturer will be responsible to:
- Keep an accurate and detailed log of all changes to their product and this log must be available to ICAR upon request. This log must include details of in-house performance measurements and Quality Assurance testing showing the product has maintained or enhanced its quality, performance and material composition.
- Submit the product for a Device Change Notification (DCN – Appendix C2) when changes are made to the composition and environmental performance characteristics of the device during its 5-year certification period. The modified device will have a new certification code, while the manufacturer will need to declare if the modified device will replace the existing one or if the two devices are going to co-exist. Every DCN application will be reviewed individually by ICAR and the designated laboratory, and ICAR shall decide if a partial test is applicable, or if the range of the modifications is such that a full test is required. Note: The request for DCN is not applicable to all types of changes to a device. Manufacturers are requested to contact the ICAR Secretariat (manufacturers@icar.org) for guidance before they apply for DCN.
- Submit the product for re-certification before the expiration of its current ICAR certification. The manufacturer must apply for re-certification no earlier than 6 months before the expiration of the certificate and no later than 5 months after the expiration of the certificate.
- Understand that within the 5 year timeframe, ICAR may take sample products from the market and test their performance against the performance of the certified device, should ICAR suspect a product change that has not been subjected to the tests outlined in procedure 5 of Section 10 of the ICAR Guidelines, or any other breach of the conditions described in this chapter.
- Should the manufacturer fail to meet any or all above certificate conditions ICAR may withdraw the certification.
- In disputes regarding the conditions above or the use of a certificate, the decision of ICAR will be binding.
- ICAR will distribute an advice notice regarding any manufacturer distributing RFID devices in conflict with the testing and certification procedures outlined in this Procedure 5 of Section 10 of the ICAR Guidelines.
